XB-IMG-127424
Xenbase Image ID: 127424
|
||||||||||
|
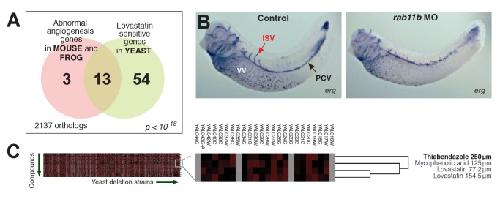
Figure 2. Identification of candidate angiogenesis inhibitors based upon genetic interactions with a yeast gene module.(A) Summary of the gene module (modified from [1]). Tests of genes associated with the yeast phenotype (lovastatin sensitivity) correctly identified novel angiogenesis genes, as in [1] and additionally shown in (B) for the gene rab11b. Morpholino (MO) knockdown of rab11B induces vascular defects in developing Xenopus laevis (frog) embryos, measured by in situ hybridization versus marker gene erg. ISV, intersomitic vein; PCV, posterior cardinal vein; VV, vitellin vein. (C) In an unbiased hierarchical clustering of compounds by their synthetic genetic interaction profiles with yeast genes (analyzing data from [13]), the action of TBZ is among those interacting with this gene module and also most similar to lovastatin, the signature compound affiliated with the angiogenesis gene module; hence, TBZ is a likely candidate angiogenesis inhibitor. Here, complete linkage clustering employing uncentered correlation coefficients is shown; additional clustering methods are illustrated in Figure S2. Image published in: Cha HJ et al. (2012) Image reproduced on Xenbase with permission of the publisher and the copyright holder. Creative Commons Attribution license
Image source: Published Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
