XB-IMG-78240
Xenbase Image ID: 78240
|
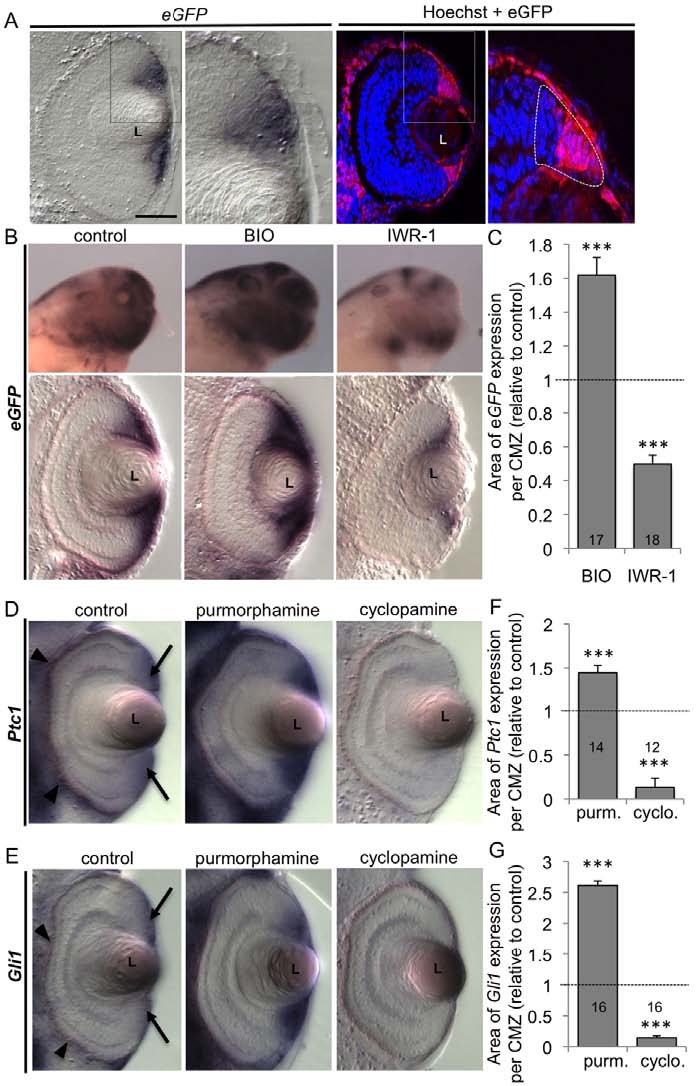
Fig. 3. BIO, IWR-1, purmorphamine and cyclopamine act as
efficient Wnt and Hedgehog pathway activators or inhibitors in
the Xenopus tadpole retina. (A)In situ hybridisation or
immunofluorescence analyses of eGFP expression on stage 40 retinal
sections from Wnt-responsive transgenic animals. Enlargements of the
ciliary marginal zone (CMZ) region (delineated with dotted line) show
that GFP expression is strongest in the peripheral half of the CMZ,
including the stem cell zone. Note that Wnt activity is also detected in
the peripheral retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). (B,C)In situ
hybridisation against eGFP on stage 40 transgenic tadpoles 24 hours
following BIO or IWR-1 treatment. (B)Representative images of staining
in whole mount (lateral view of the head) and on retinal sections
(dorsal side up). (C)Quantification of eGFP staining area per CMZ.
(D-G)In situ hybridisation analyses of Ptc1 (D) and Gli1 (E) expression
on stage 40 retinal sections 24 hours following purmorphamine or
cyclopamine treatment. Note that Ptc1 and Gli1 are detected in the
CMZ (arrows) and in the periocular mesenchyme (arrowheads).
(F,G)Quantification of Ptc1 and Gli1 staining area per CMZ. The total
number of analysed sections per condition is indicated in each bar.
***P<0.001 (Student t-test). Mean s.e.m. L, lens. Scale bar: 40m,
except 400m in whole mounts. Image published in: Borday C et al. (2012) Copyright © 2012. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher and the copyright holder. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License. Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
