XB-IMG-123986
Xenbase Image ID: 123986
|
|
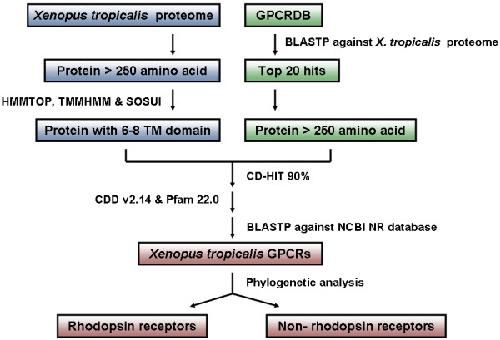
Figure 1. Sequence analysis strategy for the identification of X. tropicalis GPCRs. Two parallel methods were used for searching the crude sequence database. One was retrieval of proteins with six to eight TM domains from the X. tropicalis proteome database, and the other was extraction of the BLASTP top 20 hits by comparing the GPCR sequences from GPCRDB against the X. tropicalis proteome database. The crude database, which eliminated polymorphism, splice variants, pseudogenes and duplicates by CD-HIT 90% sequence identity, was searched for GPCR conserved domains using CDD v2.14 (E-value = 10-4) and Plam 22.0 (E-value = 0.01). The sequences with conserved seven TM domain were searched using BLASTP against the NCBI non-redundant database. Phylogenetic analyses were carried out to separate the GPCR sequences into rhodopsin like receptors and non-rhodopsin like receptors. Image published in: Ji Y et al. (2009) Copyright © 2009 Ji et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. Creative Commons Attribution license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
