XB-IMG-125353
Xenbase Image ID: 125353
|
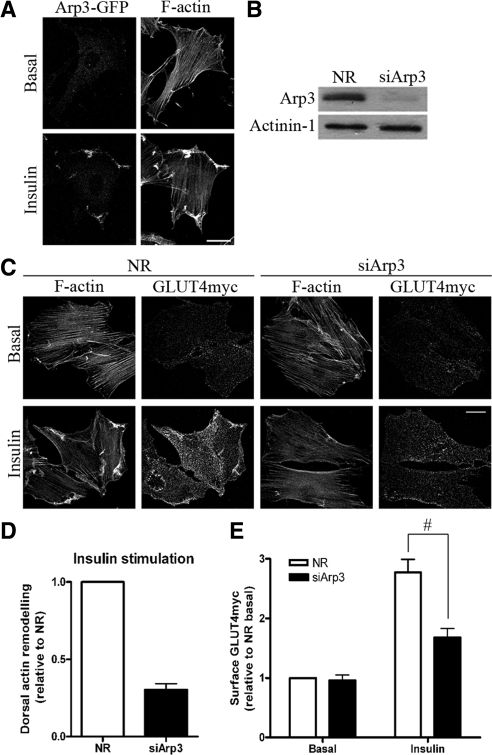
Figure 1. Down-regulation of Arp3 prevents insulin-induced actin remodeling and reduces GLUT4 translocation. (A) L6GLUT4myc myoblasts were transiently transfected with Arp3-GFP. After 3-h serum starvation, cells were stimulated with 100 nM insulin for 10 min. Subsequent staining of F-actin by rhodamine-phalloidin was performed to observe the changes in the localization of Arp3-GFP with respect to the remodeled actin. Representative images of four independent experiments are shown. Bars, 20 μm. (B) Myoblasts were transfected with 200 nM of nonrelated (NR) siRNA control or Arp3 siRNA for 72 h. Total cell lysates were prepared, and 10 μg protein was loaded and immunoblotted for Arp3 and actinin-1 (as loading control). Representative blots of five independent experiments are shown. (C) Myoblasts transfected with NR or Arp3 siRNA were treated with/without insulin for 10 min followed by staining surface GLUT4myc in nonpermeabilized cells and then permeabilized to label actin filaments with rhodamine-phalloidin. Dorsal actin remodeling was calculated from the pixel quantification in fluorescence optical cuts of the dorsal surface of adhered myoblasts (see Materials and Methods). Representative images of three independent experiments are shown. Bars, 20 μm. (D) Quantification of changes in insulin-stimulated dorsal actin remodeling relative to NR control (mean ± SE). (E) Quantification of fold increases in surface GLUT4myc relative to NR basal in NR and Arp3 knockdown conditions (mean ± SE, #p < 0.05). Image published in: Chiu TT et al. (2010) © 2010 by The American Society for Cell Biology. Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
