XB-IMG-124118
Xenbase Image ID: 124118
|
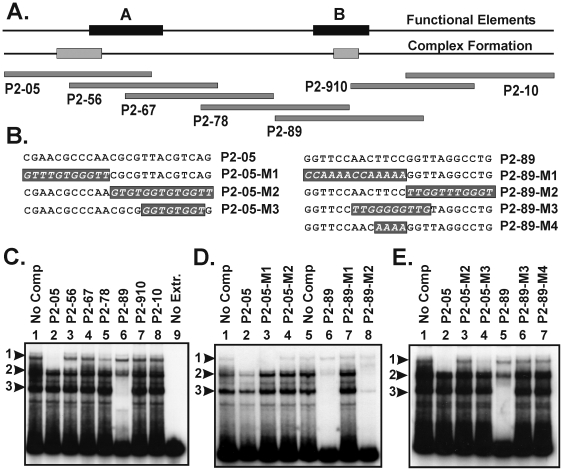
Figure 6. Identification of oocyte proteins that interact with the A and B elements.(A) A 96 bp fragment from the ALF85+ promoter was labeled and used as the probe in EMSA assays with oocyte extracts. A summary of the position of the A and B elements and the factor binding sites are shown in the two top lines. Beneath this is shown the relative locations of a series of overlapping oligonocleotide competitors. (B) An additional set of oligonucleotide competitors that contained specific mutations were also used as competitors in the binding assays. (C) Bandshift analysis shows the ALF promoter forms several protein-DNA complexes using oocyte-derived cell-free extracts. The main complexes are indicated by the labels 1, 2, and 3. The P2-05 competitor selectively abolishes complex 1 (lane 2), while the P2-89 competitor selectively abolishes complex 3 and to a lesser extent complex 2 (lane 6). (D) Additional competition assays show that P2-05-M1 but not P2-05-M2 is able to compete for complex 3 (compare lanes 3 and 4). Similarly, the P2-89-M2 competitor but not P2-89-M1 is able to compete for binding of complexes 2 and 3 (compare lanes 7 and 8). (E) Competition with mutant oligos P2-05-M3, P2-89-M3, and P2-89-M4 further refines the binding site to the positions noted in the ‘Complex Formation’ line in (A). Image published in: Li D et al. (2009) Li et al. Creative Commons Attribution license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
