XB-IMG-86901
Xenbase Image ID: 86901
|
|
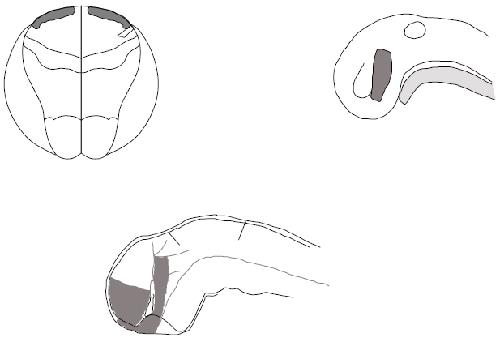
Fig. 6. Schematic summary of expression of X-dll3 at
neurula (upper left), and of X-dll3 and X-dll4 at tailbud
(upper right) and tadpole stage (lower middle). Only
expression in the neural ectoderm is shown (shaded),
based on whole-mount in situ hybridization data.The
A-P and D-V axis for the tadpole stages have been
defined in relation to the tadpole as a whole, in contrast
to other descriptions that unroll and stretch the neural
tube. Therefore, the A-P and D-V nomenclature that we
use reflects the position of structures in the tadpole
instead of their ontogenetic relationship. The
ontogenetic relationship of the tadpoleâs ventral and
dorsal forebrain is demonstrated in the neural plate fate
map (upper left) which is based on Eagleson and Harris,
(1989) and Eagleson (personal communication). This
map shows that part of the prospective ventral forebrain
originates in a more anterior position than prospective
dorsal forebrain. However, during neurulation the
forebrain undergoes a rotation movement that brings
rostral material in a more ventral and posterior position.
Also note that the dorsal telencephalon occupies a very
small area of the fate map at this stage. After closure of
the neural plate, the expression pattern of X-dll3 and Xdll4
evolves as is shown at the tailbud (upper right) and
tadpole stage (lower middle) diagram, based on tracings
of Fig. 4G,I for the tailbud stage and Fig. 4M,N and Fig. 5T for the tadpole stage. The tadpole brain diagram is based on Kuhhlenbeck,
1973, vol.3, Fig. 112. The position where the sulcus limitans ends rostrally is controversial (see Kuhlenbeck, 1973), but the present
interpretation is also consistent with the rostral extent of the basal plate as this is defined in Puelles et al. (1987). Abbreviations: cr,
chiasmatic ridge; ddi, dorsal diencephalon; di, diencephalon; dt, dorsal telencephalon; hy, hypophysis; inh, infudibular hypothalamus; me,
mesencephalon (midbrain); nt, notochord; op, olfactory placode; os, optic stalk; ov, otic vesicle; por, preoptic recess; ppr, posterior
prosencephalon; pr, prosencephalon; prv, prosencephalic ventricle; rh, rhombencephalon (hindbrain); sc, spinal cord; sl, sulcus limitans;
sm, sulcus medius; tdb, tel-diencephalic boundary; vdi, ventral diencephalon; vt, ventral telencephalon. Image published in: Papalopulu N and Kintner C (1993) Copyright © 1993. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher and the copyright holder. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License. Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
