XB-IMG-125337
Xenbase Image ID: 125337
|
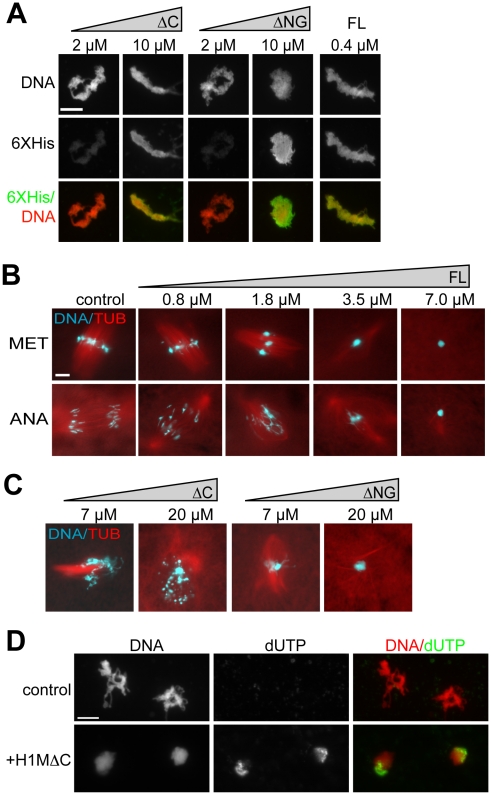
Figure 5. Overexpression Phenotypes of H1 Full Length and Domain Truncations in Extract.(A) Anti-6XHistidine immunofluorescence of chromosome clusters from reactions supplemented with increasing concentrations of amino-globular (ΔC) or C-terminal (ΔNG) H1M truncation mutants, or 0.4 µM H1M full-length (FL) as a control. Truncation mutants required much higher concentrations for efficient localization. (B) Squash fix of chromatin and rhodamine-labeled microtubules (TUB) in egg extracts supplemented with increasing concentrations of full-length H1M. Added at prophase, H1M compacts the condensing metaphase chromosomes (MET) into a single mass within aberrant spindles. Such hypercondensed chromosomes are unable to segregate during anaphase (ANA). (C) Metaphase reactions supplemented with amino-globular or C-terminal domains at high concentrations. H1MΔC causes chromosome fragmentation, while H1MΔNG causes mitotic chromosomes to compact into a single mass. (D) Representative, identically-scaled fluorescence images of sperm chromatin incubated in CSF egg extracts supplemented with biotin dUTP with or without 20 µM H1MΔC. Morphological chromatin fragmentation was less obvious using the immunofluorescence protocol, but was observed in squash samples from these reactions. Scale bars, 10 µM. Image published in: Freedman BS et al. (2010) Freedman et al. Creative Commons Attribution license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
