XB-IMG-122572
Xenbase Image ID: 122572
|
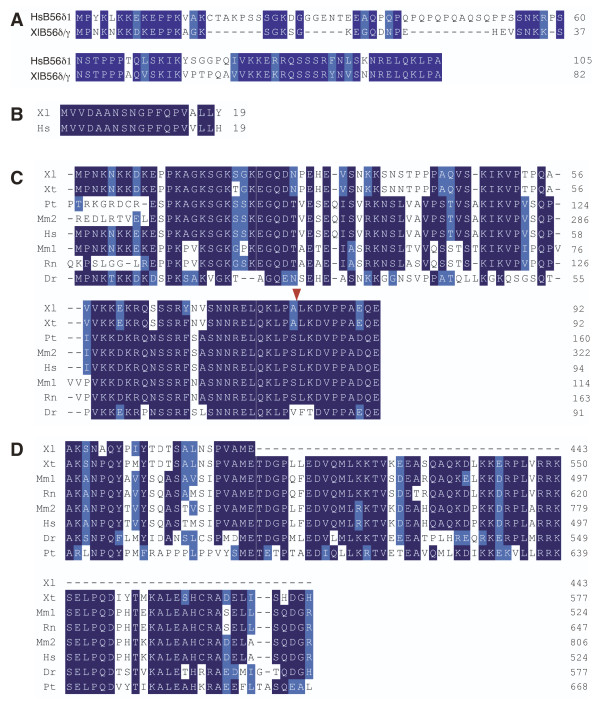
Figure 2. Alignment of B56γ amino- and carboxy-terminal variable domains. Sequence alignments are annotated as described in Figure 1. A. Alignment of Xenopus laevis B56δ/γ and human B56δ amino-terminal variable domains. B. Alignment of Xenopus laevis B56γ/γ and human B56γ amino-terminal variable domains. C. Alignment of Xenopus laevis (Xl), Xenopus tropicalis (Xt, GI:39645667), Pan troglodyte (Pt, GI:114654932), Macaca mulatta (Mm2, GI:109084945), human (Hs, GI:47077243), Mus musculus (Mm1, GI:37359748), Rattus norvegicus (Rn, GI:109478743), and Danio rerio (Dn, GI:113674011) B56δ/γ sequences from the B56δ-like amino-terminal variable region through the first ten amino acids of the B56γ core domain. The division between the variable domain and the core domain is marked by an arrowhead. D. Alignment of an alternative long form of the B56γ carboxy-terminal variable domain with the species described in C; Xenopus tropicalis (GI:45361341), Mus musculus (GI:71153488), Rattus norvegicus (GI:109478743), Macaca mulatta (GI:109084945), human (GI:31083259), Danio rerio (GI:113674011), Pan troglodyte (GI:114607473). Image published in: Baek S and Seeling JM (2007) Copyright © 2007 Baek and Seeling; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. Creative Commons Attribution license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
