XB-IMG-117547
Xenbase Image ID: 117547
|
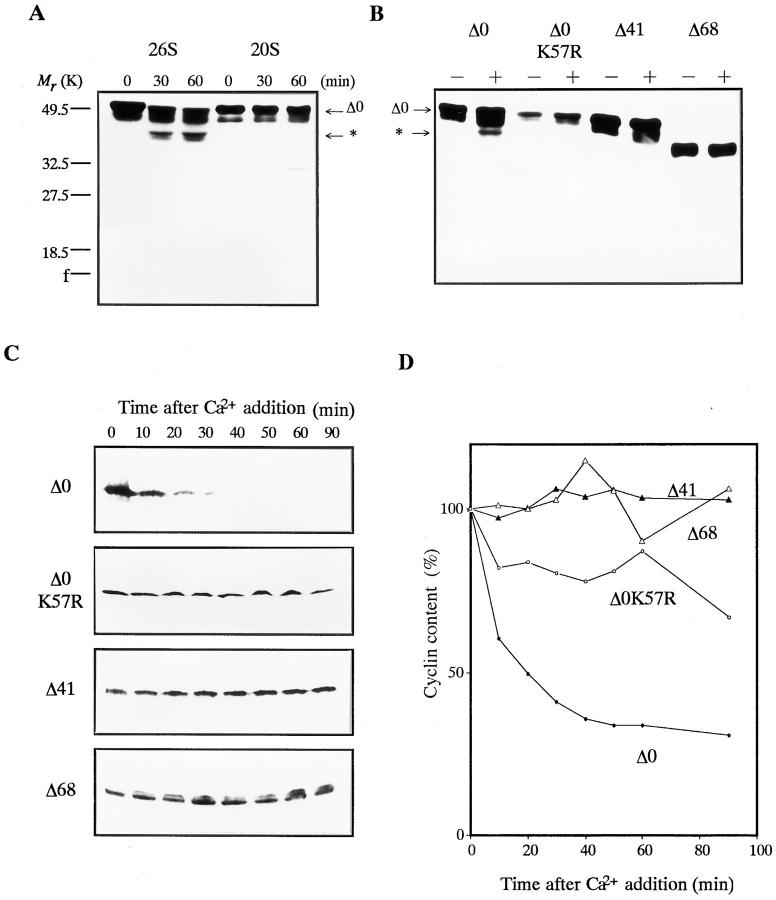
Figure 10. Digestion and degradation of in vitro translated cyclin B. The 35S- labeled cyclins Δ0, Δ0K57R, Δ41, and Δ68 were produced in vitro in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. After the translation of each cyclin, the lysate was incubated in the presence of 100 μg/ml of cycloheximide at room temperature under the indicated conditions. The 35S-labeled proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography on Imaging plates (Fuji Film). The position of the digested cyclin B is indicated by an asterisk. (A) Digestion of full length cyclin B by purified 20S and 26S proteasomes. The reticulocyte lysate containing cyclin Δ0 was incubated with 60 μg/ml of proteasomes. (B) Digestion of full length, point mutated, and NH2-terminal truncated cyclin Bs by purified 26S proteasome. The reticulocyte lysate containing cyclin Δ0, Δ0K57R, Δ41, or Δ68 was incubated in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 60 μg/ ml of the 26S proteasome for 60 min. (C) Degradation of cyclin B in Xenopus egg extracts. One ninetieth of the lysate containing cyclin Δ0, Δ0K57R, Δ41, or Δ68 was added to the Xenopus egg extracts, and its degradation was induced by 0.4 mM Ca2+. At the indicated times, the reaction was terminated by adding SDS sample buffer. (D) The same sample as in C. Cyclin contents were quantified using an image analyzer (BAS2000; Fuji Film). Image published in: Tokumoto T et al. (1997) Image reproduced on Xenbase with permission of the publisher and the copyright holder. Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
