XB-IMG-191264
Xenbase Image ID: 191264
|
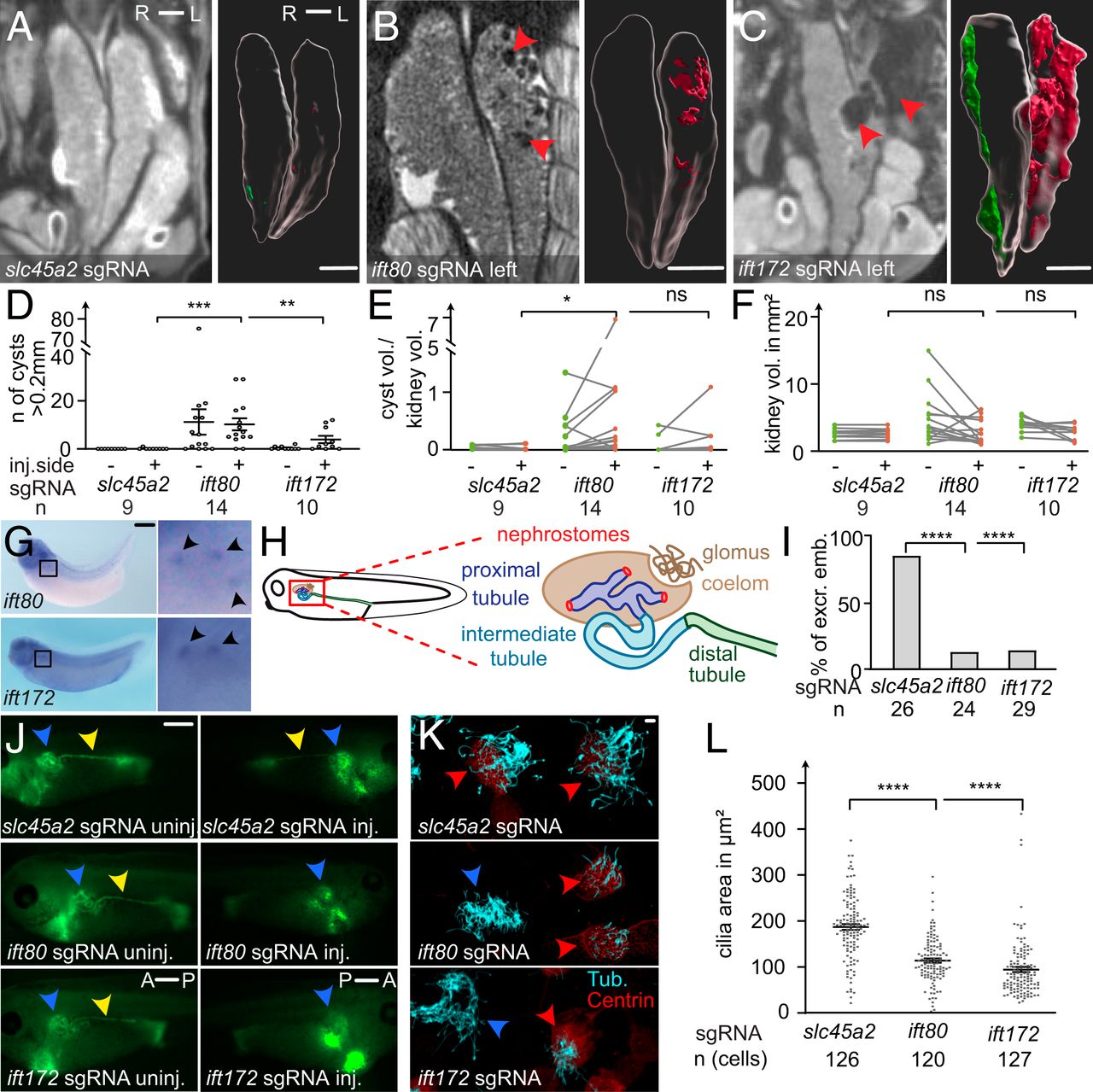
fig. 2. Cystic kidney disease and cilia defects in ift80 and ift172 CRISPRâtargeted X. tropicalis. (AâC) CRISPR/Cas9 targeting of slc45a2, ift80, and ift172 were performed unilaterally in two-cellâstage embryos. Mesonephroi of stage 61 to 63 froglets were analyzed by microCT scans and kidneys and cysts (red arrowheads in B and C) were segmented for 3D volumetric analysis; red: cysts on the injected side; green: uninjected side). (D) The number of cysts (>0.2mm), (E) the ratio of total cyst volume to kidney volume, and (F) the kidney volume (excluding cysts) was calculated and compared with kidneys of control injected animals. (G) Whole-mount in situ hybridization detects ift80 and ift172 in the multiciliated nephrostomes of the pronephros in stage 36 to 38 X. laevis. (H) Schematic depiction of the embryonic renal system of Xenopus. (I and J) Excretion assay with fluorescein-dextran at stage 38 to 40. Blue arrowheads point to the proximal part of the pronephros. Yellow arrowheads indicate fluorescence signal in the distal tubule, lacking on the injected side (J). A: anterior, P: posterior; excr: excreting; and emb: embryos. (K) Confocal images of multiciliated epidermal cells (MCCs) stained against acetylated tubulin (cyan). Centrin-RFP fusion protein served as a lineage marker (red arrowheads) and indicates CRISPR-targeted MCCs. Blue arrowheads point to nontargeted (wild type) cells. (L) The ciliated area was determined for each cell. Error bars indicate SEM. P > 0.05 ns (not significant); *P P P AâC) 1 mm, (G and I) 0.5 mm, and (L) 10 µm.] Image published in: Getwan M et al. (2021) Copyright © 2021. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher and the copyright holder. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License.
Image source: Published
Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
