XB-IMG-137164
Xenbase Image ID: 137164
|
|
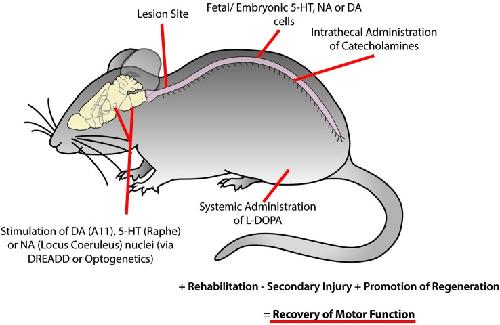
Figure 5. Recovery of motor function following spinal cord injury may be facilitated using combinatorial therapies to promote plasticity within motor networks. This could be accomplished by targeting monoaminergic systems through the activation of descending brain nuclei using optogenetic or pharmacogenetic approaches, implantation of fetal or embryonic cells from the dopaminergic ventral tegmental area, noradrenergic locus coeruleus or serotonergic raphe nucleus caudal to the site of injury, intrathecal injection of catecholamines and systemic injection of L-DOPA. While these approaches may not be optimal in isolation, they may serve as an effective complementary treatment with rehabilitation and other therapies to reduce secondary injury and promote regeneration of damaged descending tracts to promote the recovery of motor function. Image published in: Sharples SA et al. (2014) Copyright © 2014 Sharples, Koblinger, Humphreys and Whelan. Creative Commons Attribution license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
